Remove and Scrap Link Enhancement
The enhancement in 9.3 creates a more explicit system link between the "remove" and "scrap" functions which were previously two interrelated but not properly connected transactions. This makes it easier to track how a scrap originated or what happened when something was removed from a parent product.
The change is especially important for users doing loss analysis, as it allows them to relate the removal of an item directly to its subsequent scrapping, improving traceability and reporting.

Job Document Traceability
In 9.3 there is now a revision history available relating to any changes made to job document version links.
Electronic Control History Record (eCHR) Enhancements
Further enhancements have been made to the eCHR.
Add [BLANK] values in eCHR Listing
In a paper DHR, the person completing the paperwork must ensure there are no empty fields and will normally write N/A if a field genuinely is intended to be blank.
In the eCHR, where the information is blank by design and cannot be changed by the operator, e.g., the entity has been checked and approved as part of the definition of manufacture (e.g., no upper / lower tolerance on an approved BoM slot) this can be automatically populated with ‘[BLANK]’ in the eCHR as of 9.3.


Where the information is transactional and under the control of the user, the system will not automatically insert data. The end user must input ‘N/A’, so the output of these fields should not be altered by the query. If the field is blank, it means it has been missed.
Additional trigger for issue line type - Job Issue
A job-linked issue will trigger an inclusion in the eCHR when an issue is created or updated that is linked to the job on which any items in the eCHR are being processed. The configuration has the option to specify a job issue type to be included in the eCHR (if null then all job issues will be captured).


Approval of a workflow version - eCHR partial complete vs split validation
The enhancement adds validation to ensure that when approving a workflow version, the eCHR setup is not invalid.
Specifically, if a workflow is set up to allow splitting during partial completion, the eCHR profile must also be configured to record splits; otherwise, the system will prevent approval to avoid incomplete setups.
This ensures consistency and data integrity as splits, serial number changes, and similar actions are critical to be tracked in the eCHR for accurate records.
The validation helps prevent scenarios where serial numbers or splits would not be properly recorded due to misconfiguration.
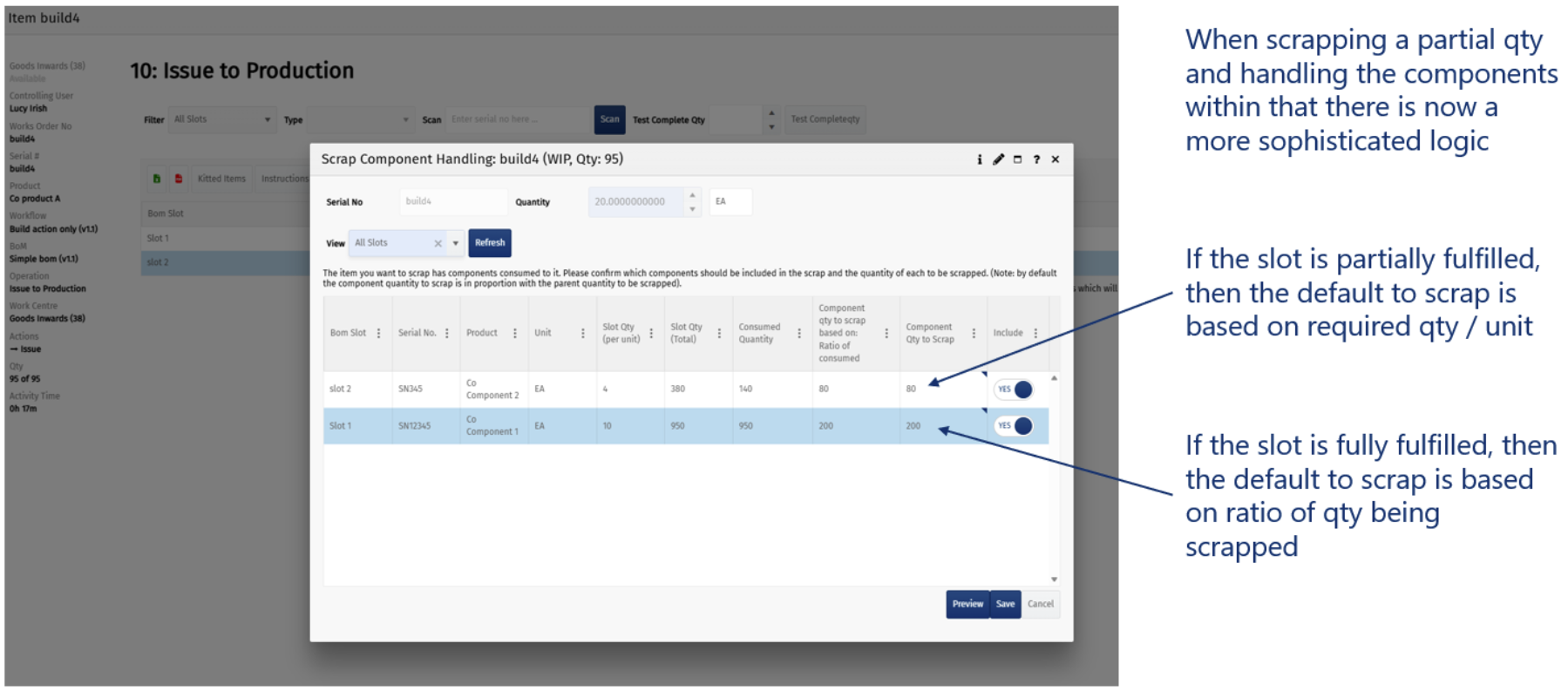
New Split Mode for New UI for WIP Splitting
The logic for handling material splits during scrapping (see What’s New 9.1) has been improved to use “ratio-based” calculation when a slot is fully satisfied, and “required-based” calculation when only partially satisfied.
This change addresses previous issues where using only ratio logic led to impractical results, especially with whole-number components (e.g., buttons on a radio).
The enhancement provides more accurate and sensible handling of component consumption and scrapping, especially in scenarios where builds are ongoing and not all slots are fully satisfied.
Public API
Upsert on Unique fields
You can call the following upsert endpoints without an ID (where the entity exists then the ID is retrieved from the unique field, i.e., name).
/api/Recipe/Upsert
/api/BOMSlot/Upsert
/api/BOMSlot/UpsertCandidates
/api/BOMSlot/UpsertProperties
/api/BOM/Upsert (v2)
API changes to support Job Specific BoMs
Improved functionality for handling job specific BoM versions.
Added the `bom` and `bomversion` ID to the response payload for schedule upsert.
Added BoM slot properties to the v2 bom upsert.
Customer/Supplier Links
Ability to create organisation/product links through the Product Public API.
Ability to create organisations as needed.
Assign Work Centres to Line Config
It’s possible to assign work centres to a Line Config in the api/WorkCentre/Upsert endpoint.
BoM Upsert
It is no longer required for each section in the payload to reference a parent section.
Workflow (Header)
Added List, Upsert and Delete endpoints.

Added Workflow Type upsert, and delete endpoints.

Workflow Version
Moved the api/WorkflowVersion/List upsert under the new WorkflowVersion section. Also added upsert and delete endpoints.

Integration
Email notifications on integration manager
It is now possible to configure a list of users and the statuses they want to receive notifications for. Notifications are sent via email or in-app notifications.

Quality
Checklist Version Report
Checklists were enhanced as follows:
It has been made easier to find any checklists related to a given product. If you use the new product search box the correct Product Type will be automatically populated in the Product Type search, allowing you to quickly find any related checklists.
It is now possible to see any tool requirements that are linked to checklist steps. Tool requirements are now hidden columns in the Checklist Steps pop-up.

Additional Configuration options for 'Comments' on Check List Steps
New configuration options have been added for checklist steps, allowing comments to be set as not needed, optional, or compulsory.

The “Compulsory if Blank Result” option requires a compulsory comment if a result is not entered, ensuring operators acknowledge skipped steps and provide a reason.
This serves as a workaround for scenarios where conditional checks are not yet supported, helping maintain accountability and clarity in process documentation. Example use case could be if there are 2 checks for a given check item template in normal circumstances but a further 2 may be done if any of the first two are marginal. In this situation, the additional steps can be optional but require a comment to say ‘not required’ if not used.
Recipes
In version 9.3, users possessing the appropriate permissions may revert recipes from Obsolete status to Approved.
Note that reverting a controlled recipe from Obsolete to Draft status is not permitted, as this would circumvent proper controls for making modifications. Where a workflow is uncontrolled, you can change from Obsolete to Draft status.
Reports
OEE Detailed Analysis in Power BI
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) calculations are based on the calculations described in the image below.

The “OEE Analysis” report has been renamed to “Top Line OEE Analysis” which displays a summary report for OEE.
In 9.3, the “OEE Detailed Analysis” report was created. This is a BI report that allows you to construct your own report from the data points you choose.

OEE Menu restructure
The Overall Equipment Effectiveness menu was added and structured to improve usability.

Additional tab for Actual vs Planned on Work Centre Actual vs Standard Report
The system now supports analysis of actual versus planned times at the work centre level, in addition to the previous actual versus standard time comparison.
This allows users to identify which operations, jobs, or products consistently differ from their planned times, helping refine planning accuracy.
Planned times are intended to reflect real-world performance and are more flexible than standard times, which are typically fixed for budgeting and business planning.
The enhancement is important for improving operational efficiency and ensuring that plan times are regularly updated to match actual performance.

Scrap Analysis Report
The Scrap Analysis report was enhanced to view WIP and component scrap percentage by works order with reason codes, and it filters by scrap entry timestamp, scrap entry shift, scrapped product name, works order number, scrap type, Operation Scrap %, Job Scrap %.


Scheduling
Job Operation Plan Property
You can store additional information against individual operations within a job plan, which is particularly useful when integrating with external planning or ERP systems.
For example, companies using external tools planning systems can now record which specific tool should be used for each operation, addressing a previous gap where only work centre capacity was planned, not tool allocation.
This is achieved by creating a plan property (e.g., "use this tool") that can be populated for each operation, improving flexibility and supporting more complex planning scenarios.
The enhancement is valuable for organisations with specialised requirements, such as large warehouses of moulding tools, and can be adapted for other types of additional operational data.
Tools
Silent Tool Use
Previously, we could set up an action for a tool use and record which tool was used. However, if the operation is long-running and you need to track how many times the tool cycles, a single action won’t work. You don’t know in advance how much will be produced, so you can’t predict the number of tool cycles.
For example, suppose you have a mould tool that produces 10 units per cycle. This may potentially be installed in the work centre before the works order is started as part of a preparation/setup step and potentially by a different team to the operations team. If you make 100 units in shift 1, 100 in shift 2, and 100 in shift 3, you need to record tool usage each time you record a quantity because tool usage depends on production quantity.
In 9.3 you can now use a silent tool use action. This allows you to specify a tool requirement (or requirements) that the system will automatically record tool uses against, based on a logic you can configure (fixed/cycles per unit produced). When you use a silent tool use, you must locate a single tool of the type specified with the work centre location. The system will then know which tool to record use logs against.
Once that’s set up, every time you complete a quantity, the system automatically tracks tool usage behind the scenes. It knows how many cycles occurred based on the quantities produced (or a fixed number of uses for the total qty if configured that way).

Note on cycles per unit of production: This is the number of cycles needed to process a single unit of output by design e.g. a moulded part will only typically need one cycle of the mould tool to make, whereas a stamped part might require two cycles to fully shape and separate.
Modular Tool Type - modelling of tool elements (e.g. cavities / inserts / cores)
Modular tools are tools that might contain several different elements that can all process items at the same time.
'Element' is a catchall word for the modular components such as inserts, cavities, pockets, etc., that can be attached to a tool required for the tool to be used.
The production rate of output is determined by the number of cavities. If you're a cavity down, your output will be impacted. The number of cavities, inserts, etc. determines the ratio of production to tool cycles. This is important if the tool’s maintenance plan is based on the number of cycles. Example is a mould tool which has 100 cavities – this can mould 100 items every time it cycles. If one cavity is damaged or faulty it is removed and therefore the mould tool can only mould 99 items every time it cycles. A job for 1000 items would take 10 cycles of the fully functioning tool to complete - it would take 11 cycles to complete if one of the cavities were removed.
In 9.2, a modular tool can be modelled as a tool type in the system, with the options to specify:
The name of the elements that go into the tool (e.g., cavities / inserts / cores).
The maximum number of elements that the tool can be made up of.
The current number of elements actually in place.
The use count of a modular tool can then be based on the combination of the output from a machine divided by the max elements or the current elements if this is populated.
If the tool use action requirement is configured as ‘cycle per unit of production’:
Calculation of the number of tool uses = No. Cycles per unit of production * units produced / number of active elements in the tool.
Note if tool use action is configured as ‘fixed’, this will be a fixed number of tool uses for the item (regardless of qty of the item) and will be recorded at first completion.
Tool Move UI and Transaction
A dedicated UI has been added for moving tools, accessible from both the workstation screen and the tool manager, making the process more intuitive.
Previously, users had to use the "edit tool" function to move tools, which was not user-friendly or logical for this purpose.
The enhancement streamlines tool management and addresses usability issues highlighted by the introduction of silent use functionality.
Show tool total use count in maintenance management grid as hidden field
In previous versions, it was possible to only see a tool’s use count since its last calibration. In 9.3, a hidden field was added to the Maintenance Management screen that shows the total use count for the tool.
 `
`
Workflow
Display eSign requirement and eSign status against workflow versions
The workflow grid now shows the eSign requirements and eSign status.
Three columns were added:
Against the Workflow level of the tree list:
Controlled: Indicates if the Workflow Type is controlled (Yes / No).
Requires eSignature: Indicates if the Workflow Type requires an eSignature (Yes / No).
Against the workflow version level:
eSigned: Indicates if the version was signed (Yes / No / N/A (N/A if eSignature is not required)).


